Quantitatively, the International Energy Agency (IEA) previously released the “Special Report on Photovoltaic Global Supply Chain”, which shows that since 2011, China has invested more than 50 billion US dollars to expand the production capacity of photovoltaic equipment, which is 10 times that of Europe. China has created more than 300,000 manufacturing jobs; China's photovoltaic manufacturing industry occupies at least 80% of the global production capacity in all production links of solar panels, from silicon materials, silicon ingots, wafers to cells and modules, among which the lowest The highest is silicon material (79.4%), and the highest is silicon ingot (96.8%). The IEA further predicts that by 2025, China's production capacity in certain links will account for 95% or more.
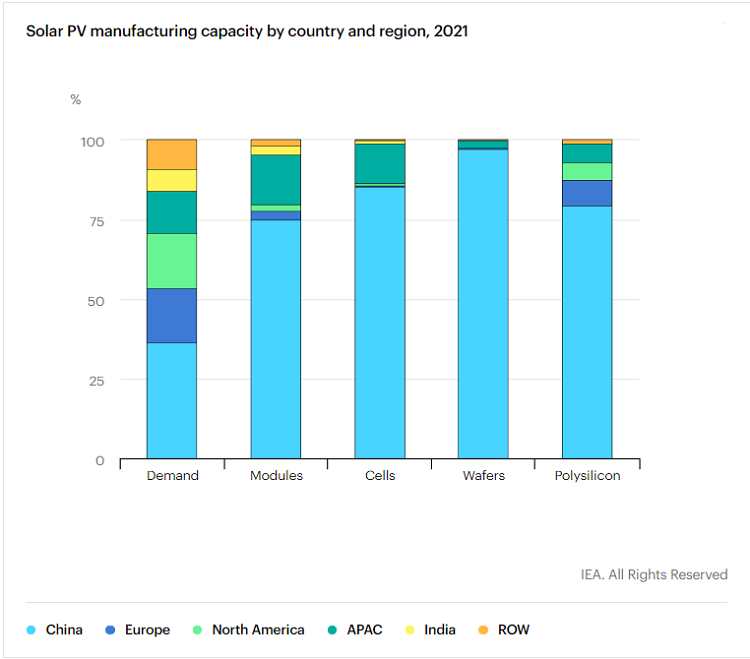 No wonder the IEA will use "dominate" to describe the status of China's photovoltaic industry, and even claim that it poses a certain threat to the global photovoltaic supply chain.“…the level of geographical concentration in global supply chains also creates potential challenges that governments need to address.”If you look at it qualitatively, it is even more interesting that a commentary in the "New York Times" regards China's photovoltaic industry as a major threat. The last "threat theory" may still be 5G. 
But solar panels are not the only link in the PV value chain dominated by Chinese companies. This article focuses on another lesser-known, but equally critical device in photovoltaic power generation systems—the photovoltaic inverter.
Inverter, the heart and brain of photovoltaicsThe photovoltaic inverter can convert the direct current generated by the solar cell module into alternating current with adjustable frequency and can be used for production and life. The inverter is also responsible for maximizing the power generation capacity of the photovoltaic panels and providing system fault protection, including but not limited to automatic operation and shutdown functions, maximum power tracking control functions, a series of functions required by grid-connected systems, etc.
In other words, the core function of the photovoltaic inverter can also be summarized as tracking the maximum output power of the photovoltaic module array, and feeding its energy into the grid with the smallest conversion loss and the best power quality. Without the "heart and brain" of this photovoltaic system, the electricity produced by current solar cells would not be available to humans.
From the perspective of the position of the industrial chain, the inverter is located in the downstream of the photovoltaic industry, and it enters the link in the process of building a power generation system (no matter what form).
The current photovoltaic inverters have a variety of classification methods, which are more common and easy to understand, and are distinguished by product types. There are mainly four types: centralized, string, distributed and micro inverters. Among them, the micro-inverter is quite different from the other three devices, and can only be used in small photovoltaic power generation systems, such as home photovoltaics, and is not suitable for large-scale systems. From the perspective of market share, string inverters have taken an absolute dominant position, centralized inverters ranked second with a large gap, and other types accounted for very little. According to the data given by CPIA, string inverters account for 69.6%, centralized inverters account for 27.7%, distributed inverters have a market share of about 2.7%, and micro inverters are not visible. statistics. 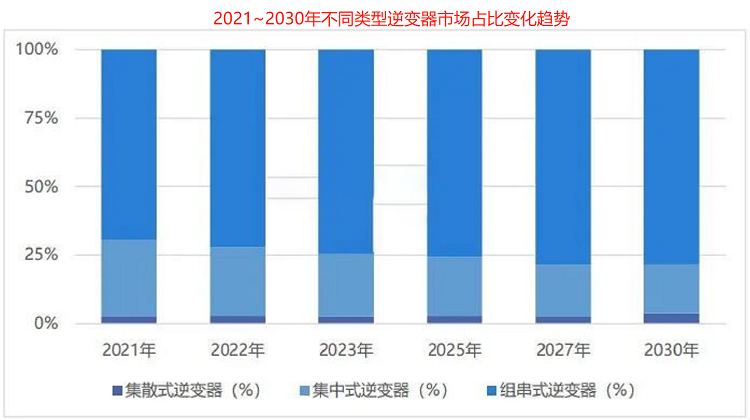 The reason why the current most mainstream inverter products are of the string type is that: the operating voltage range is wide and the power generation capability is strong in low light; a single inverter controls few battery components, generally only dozens, which is much smaller than the centralized inverter The number of thousands of generators, the impact of unexpected failures on the overall power generation efficiency is relatively low; the operation and maintenance costs are low, the fault detection is relatively easy, and when a fault occurs, the troubleshooting time is short, and the failure and maintenance cause less loss.
However, it needs to be emphasized that in addition to large-scale power plants, the photovoltaic industry also has numerous specific application scenarios, and there are many types of distributed photovoltaics, such as household photovoltaics, factory roof photovoltaics, high-rise building photovoltaic curtain walls, and so on. For such photovoltaic power generation facilities, the state also has corresponding plans. For example, in the Implementation Plan for Carbon Peaking in Urban and Rural Construction issued by the Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development and the National Development and Reform Commission in July, it is mentioned that by 2025, new public institution buildings, The roof photovoltaic coverage rate of the newly built factory building will reach 50%. Different application scenarios have different needs for photovoltaic inverters, and with the rapid development of the photovoltaic industry, the impact of technological iterations on the industry cannot be ignored, making the market structure of photovoltaic inverters uncertain.
In terms of market size, it should be stated that because more than one leading company in the inverter industry has not been listed, the incomplete information disclosure has caused certain statistical difficulties, resulting in certain differences in the data given by different institutions due to the influence of caliber.
From the perspective of market size, according to the statistics of shipments: IHS Markit's PV inverter shipments in 2021 are about 218GW, a year-on-year increase of about 27%; Wood Mackenzie's data is more than 225GW, A year-on-year increase of 22%.
The reason why the current photovoltaic inverter industry has considerable competitiveness is mainly due to the considerable price advantage brought by the stable cost control ability of domestic enterprises. At this stage, almost every type of inverter in China has a fairly obvious cost advantage, and the cost per watt is only about 50% or even 20% of the overseas cost.
Cost reduction and efficiency increase is the direction of optimizationAt this stage, domestic photovoltaic inverters have established a certain competitive advantage, but of course this does not mean that there is no possibility of further optimization in the industry. The main cost reduction paths for future photovoltaic inverters will focus on three aspects: localization of key components, power density improvement and technological innovation.
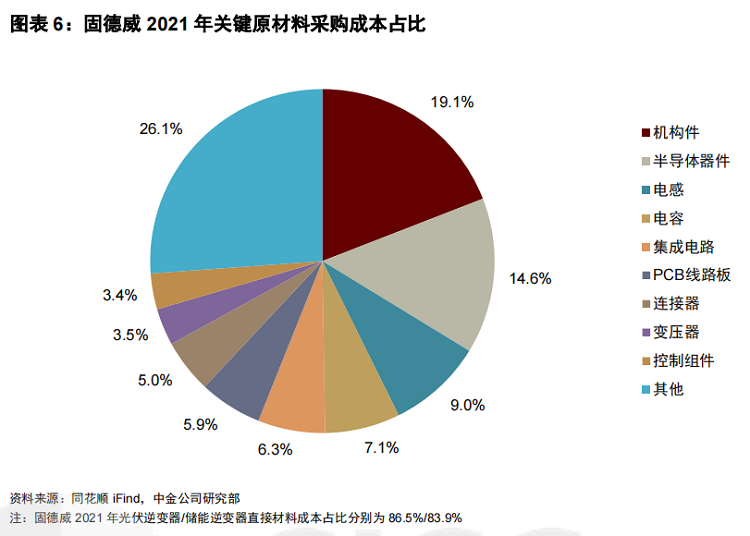 In terms of cost structure, the direct materials of photovoltaic inverters account for a very high proportion, exceeding 80%, which can be roughly divided into four parts: power semiconductors (mainly IGBTs), mechanical parts (plastic parts, die castings, radiators, Sheet metal parts, etc.), auxiliary materials (insulating materials, packaging materials, etc.), and other electronic components (capacitors, inductors, integrated circuits, etc.). The general price of materials used in photovoltaic inverters is significantly affected by upstream raw materials, the production difficulty is not high, the market competition is already sufficient, further cost reduction is difficult, and the bargaining space is relatively limited, which can not provide much help for further cost reduction of inverters . But semiconductor devices are different. Power semiconductors account for 10% to 20% of the cost of the inverter. They are the core components to realize the DC-AC inverter function of the inverter, and directly determine the conversion efficiency of the equipment. However, due to the high industry barriers of IGBTs, the level of localization at this stage is not high. This makes power semiconductors have stronger pricing power than other devices. It is also the global semiconductor shortage and price increases since 2021 that have led to obvious pressure on the profit of inverters, and the gross profit margin of products has mostly declined. With the rapid development of domestic semiconductors, the inverter industry is expected to realize the localized replacement of IGBTs in the future and achieve overall cost reduction.
The increase in power density refers to the development of products with higher power under the same weight, or lighter products under the same power, thereby diluting the fixed costs of structural parts/auxiliary materials and achieving relative cost reduction results. From the perspective of product parameters, the current various inverters are indeed constantly improving the rated power and power density.
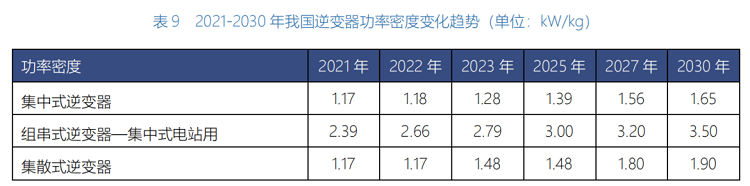
Technological iteration is relatively straightforward. The inverter industry can achieve cost control and further open up profit margins by further optimizing product design, reducing materials, improving production processes, and switching to more efficient devices.The next world, energy storage?In addition to photovoltaics, another market direction of the current inverter industry is the equally hot energy storage.
Photovoltaic power generation, especially distributed photovoltaic systems, has natural intermittency and volatility. Connecting to energy storage systems to achieve continuous and stable power supply is a widely recognized solution.
In order to meet the needs of the new power system, the Power Conversion System (PCS; sometimes referred to as the energy storage inverter for the convenience of understanding) came into being. PCS is an electrochemical system that connects the battery system and the power grid to realize bidirectional conversion of electric energy. It can not only convert alternating current into direct current to charge the battery during the load trough, but also convert the direct current in the storage battery into alternating current during the peak load period and connect to the grid. .

However, due to the more complex functions, the power grid has higher performance requirements for energy storage inverters, resulting in a substantial increase in the number of components used, which can be nearly twice that of ordinary photovoltaic inverters. At the same time, the complex functions also bring higher technical barriers.
Correspondingly, although the overall scale is not very large, the energy storage inverter has already shown excellent profitability, and the gross profit margin has a considerable advantage over the photovoltaic inverter.
Judging from the current situation of the industry, the overseas energy storage market started earlier, and the demand is stronger than that in China. Domestic companies have not yet established a market dominance similar to that of battery components and inverters in the industry. However, the market scale of energy storage inverters at this stage is not large, and there is a huge gap with photovoltaic inverters. There is no obvious difference in competitiveness between domestic and foreign companies, which is mainly the result of business choices.
For enterprises, although there are certain technical barriers, the technology of energy storage inverters and photovoltaic inverters has the same origin, and it is not very difficult for enterprises to transform. And in the domestic market, driven by both industry and policy, the energy storage industry has entered a period of rapid development, with considerable market growth and strong industry certainty, which is a very clear business development direction for inverter companies.
In fact, many companies have benefited from the good expectations of the energy storage industry. Judging from the performance in 2021, the energy storage business lines of many companies have shown strong growth. Although this growth has a certain relationship with the low base, it is enough to prove that the development of energy storage-related equipment manufacturing has strong certainty, and there is no doubt that it has good business logic and growth.
The future cost reduction route of energy storage inverters is also relatively clear, which is not very different from photovoltaic inverters. It focuses on reducing the price of components, especially the localized replacement of power semiconductors. Since the number of components used is much larger, domestically produced The cost-reducing effect brought by the substitution can be further magnified.
If inverter companies accelerate the development of energy storage converter products, relying on the rapid development of the energy storage industry and the established competitive advantages of grid-connected inverters, we have every reason to believe that the local industry has every opportunity to rely on China's The advantages of manufacturing, the reproduction of the prosperity of the photovoltaic industry in the energy storage value chain, and the commercial success of domestic enterprises are also natural results. 
|

 6 Keji west road. Hi-Tech Zone Shantou City, GuangDong,China
6 Keji west road. Hi-Tech Zone Shantou City, GuangDong,China +86-0754-81888658
+86-0754-81888658 multifit@multifitele.com
multifit@multifitele.com